Network-forming Oxides Which Are Compounds That Use Additional Molecular Bonds
Covalent Bonds Compounds and Molecules. Certain organic compounds react with oxygen or other oxidizing agents to produce substances called oxides.

Chemical Bonding Molecular Shapes And Vsepr Theory Britannica
Bridging Oxygens link glass forming tetrahedra.

. A network solid or covalent network solid is a chemical compound in which the atoms are bonded by covalent bonds in a continuous network extending throughout the material. Ionic bonds form between two atoms that have different electronegativity valuesBecause the ability to attract electrons is so different between the atoms its like one atom donates its electron to the other atom in the chemical bond. Lab 15 -- Activity Naming Chemical Compounds I.
Paulings packing rule. Exists as a repeating pattern. Formulas for network solids like those for ionic compounds are simple ratios.
A network of interconnected atoms. Most covalent molecular structures have low melting and boiling points. Thus amines phosphines and sulfides form amine oxides phosphine oxides and sulfoxides respectively in which the oxygen atom is covalently bonded to the nitrogen phosphorus or sulfur atom.
When waste ions assumed to be present as oxides or as compounds that form oxides upon melting in air are incorporated in borosilicate glass they are normally incorporated as network formers or network modifiers and the waste oxides can simply be added to the precursor glass chemicals which are usually in the form of glass frit produced by pouring the molten glass into. The positive ion called a cation is listed. Depositing pyromellitic acid through ultrahigh-vacuum physical vapor deposition on a metal-oxide and metal-aluminate system.
It is thermally stable. In a network solid there are no individual molecules and the entire crystal or amorphous solid may be considered a macromolecule. Cl 2 O 7 covalent.
132 CHAPTER 4 Molecular Compounds ADDITIONAL PROBLEMS 433 STRUCTURAL FORMULAS SECTION 46 444 Distinguish between the following. Network-modifying oxide growth is attributed to outward metal ion migration to the oxide-electrolyte. You can recognize ionic compounds because they consist of a metal bonded to a nonmetal.
When the metal oxides are exposed to an external stress such as heating the compound remains sound ie. Each carbon atom forms covalent bonds with three other atoms to form two-dimensional layers. Recognizing Compounds With Ionic Bonds.
Modified the addition of the second oxide. These ionic compounds are called Glass Modifiers. A A molecular formula and a structural formula b A structural formula and a condensed structure c A lone pair and a shared pair of electrons 445 Assume that you are given samples of two white.
Ionic compounds form when positive and negative ions share electrons and form an ionic bondThe strong attraction between positive and negative ions often produce crystalline solids that have high melting points. Among the noble-gas elements xenon has the most extensive chemistry and it can possess formal oxidation states of 0 2 4 6 and 8 in its compounds by forming fluorides oxides and oxide fluorides as well as derivatives in which xenon is bonded to polyatomic groups through oxygen nitrogen and carbon. Graphite intercalation compounds GICs are formed by the insertion of atomic or molecular layers of a different chemical species such as alkali metal atoms or acid molecules as atoms or molecules called the intercalant between host graphite sheets 103 see Figure 10.
Boron carbon and silicon are all examples of covalent network elements. This is because the intermolecular forces between covalent molecules require a lower amount of energy to separate from each other. Octahedral CN preferred in Al2O3.
Classification of compounds A. The enthalpy of fusion is the amount of. Peroxides retain some of oxygens original molecular structure O-O White or light yellow sodium peroxide Na.
The input factors for neural network training came from multiple validated in silico models and the resultant networks attempted to predict features of the results from existing models. Chemical bonds are generally divided into two fundamentally different types. Given that the networks were trained only on phosphine and phosphine oxide compounds these networks may have limited use on compounds outside this class.
Metals with very low reactivity form weak bonds with oxygen and these metal oxides tend to decompose relatively easily when heated. In reality however the bonds in most substances are neither purely ionic nor purely covalent. Diamond and graphite two forms of carbon and compounds like silicon dioxide and silicon carbide are all.
Nonbridging Oxygens form the ionic bonds with the modifiers 3. Exist as individual molecules. The study of the influence of vulcanizing systems with the participation of metal oxide on the intrinsic viscosity η char showed that in comparison with other used oxides there is observed an increase in the molecular weight containing zinc oxide which is released from other used metal oxides CaO MgO and CdO depending on the time of.
Layers stack on top of one another like sheets of paper and can slide past one another easily. Highly reactive metals form strong bonds with oxygen to form metal oxides. Formulas are the ACTUAL numbers.
Covalent molecular compounds usually have a low enthalpy of fusion and vaporization due to the same reason. Lonic compounds 1 Binary ionic - contains two elements a metal and non-metal held together by lonic bonds 2 Temary lonic - compound contains three elements with at least one metal and one non metal held together by at least one ionic bond B. 2c d indicating the formation of physical and chemical bonds as opposed to the case of DCC.
Types of Covalent Bonds. The rest of the Earths crust is formed also of oxygen compounds most importantly calcium carbonate in limestone and silicates in feldsparsWater-soluble silicates in the form of Na4 SiO 4 Na 2 SiO 3 and Na 2 Si 2 O 5 are used as detergents and adhesives. The force of attraction between oppositely charged ions that result when the more electronegative atoms takes electrons from the less electronegative ion.
Violates Zachariasens rule 1. Formulas are the simplest ratio of 1 to another. In contrast passive layers on metals other than aluminum are classified as network modifiers forming a multilayered oxide film of progressive stoichiometry such as cobalt oxide which forms an inner divalent oxide layer and an outer trivalent oxide layer CoCoOCo 2O 3.
Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds. Self-assembled molecular network formed by controlling molecular deposition of organic compounds. Ionic bonds form instead of covalent bonds when there is a large difference in electronegativity between the ions.

Molecular Main Group Metal Hydrides Chemical Reviews

Ionic Solids Molecular Solids Metallic Solids Network Covalent Solids Atomic Solids Youtube

Permanganyl Fluoride A Brief History Of The Molecule Mno3f And Of Those Who Cared For It Schmidbaur 2021 Chemistry A European Journal Wiley Online Library

Mineral Chemical Bonding Britannica

Metal Free Cross Dehydrogenative Coupling Cdc Molecular Iodine As A Versatile Catalyst Reagent For Cdc Reactions Parvatkar 2019 Chemistry 8211 An Asian Journal Wiley Online Library
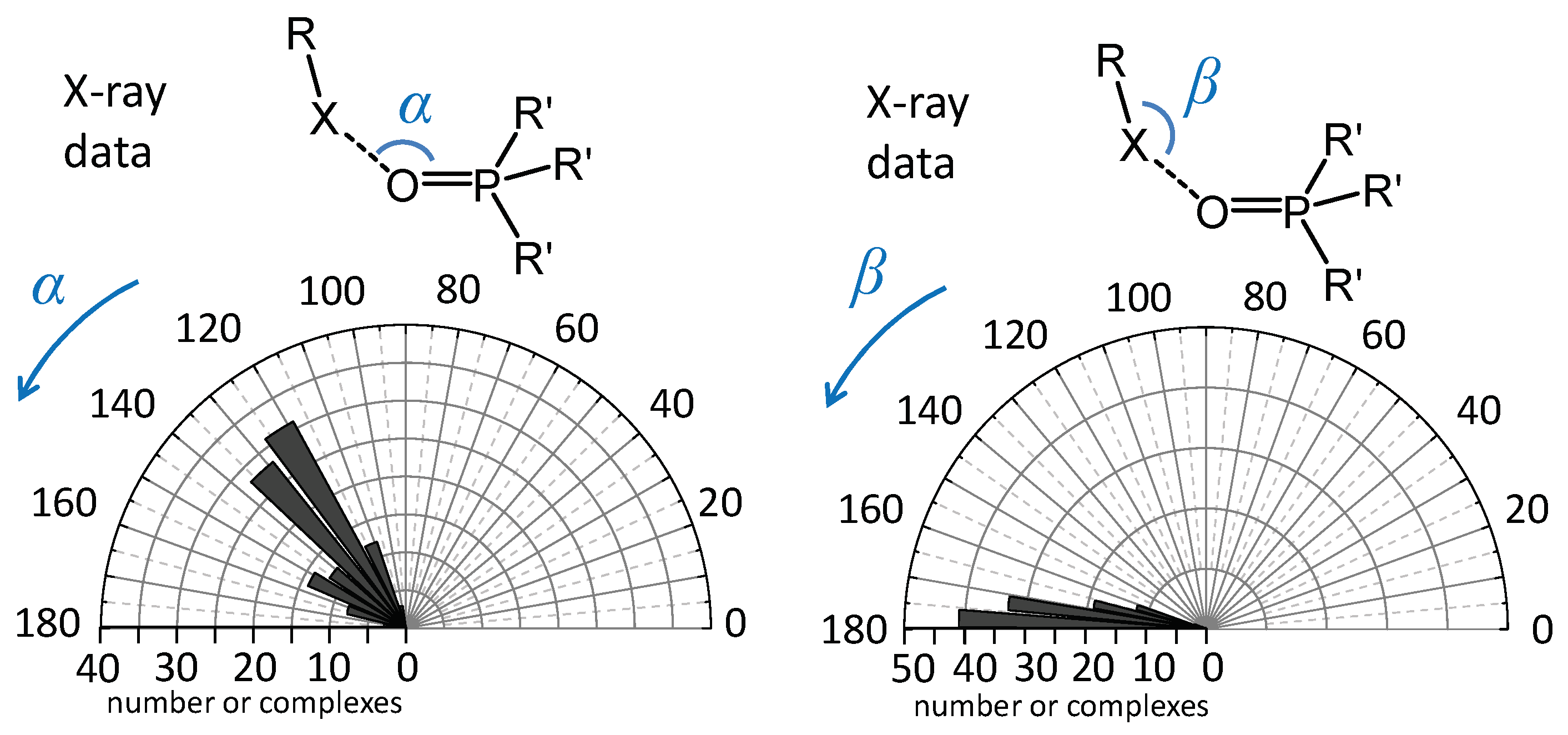
Molecules Free Full Text Phosphine Oxides As Spectroscopic Halogen Bond Descriptors Ir And Nmr Correlations With Interatomic Distances And Complexation Energy Html
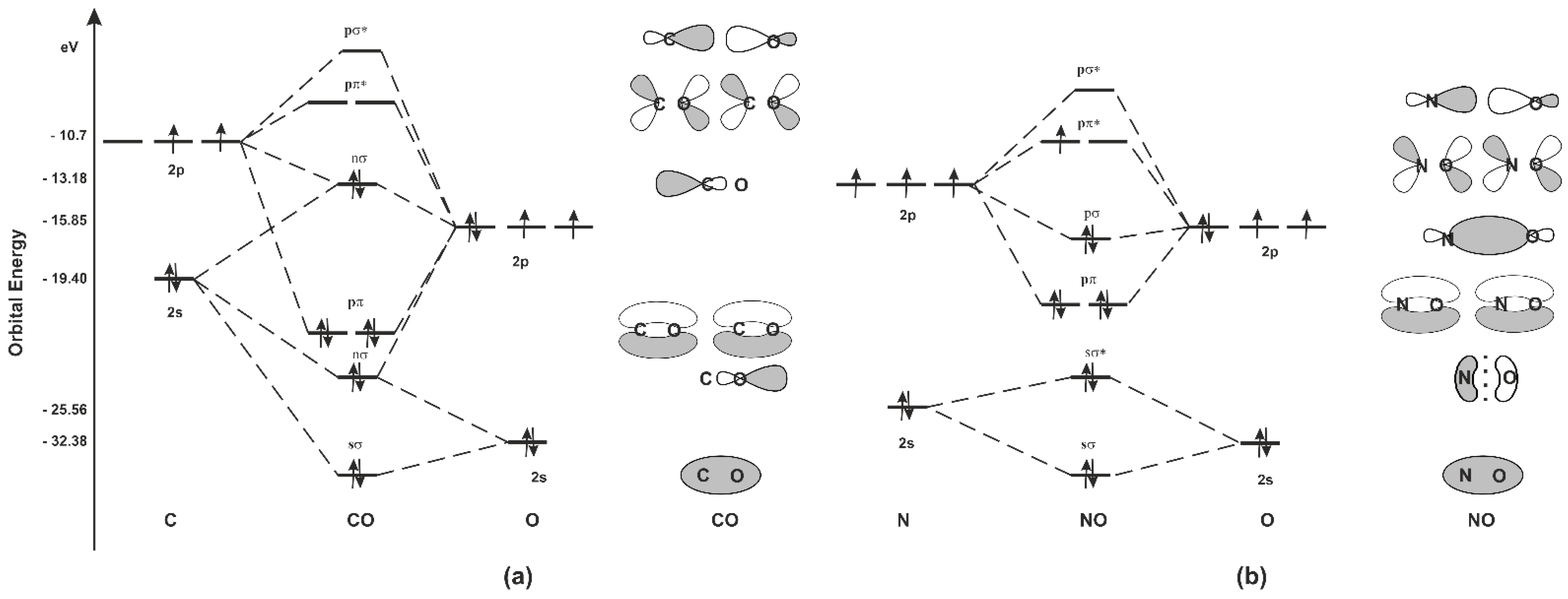
Ijms Free Full Text Carbon Monoxide And Nitric Oxide As Examples Of The Youngest Class Of Transmitters Html

Borane Description Structure Facts Britannica

The Reactivity Series Of Metal Carbon And Hydrogen Are Not Metals But They Are Shown For Compariso Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Lessons Gcse Science Revision

Molecules February 1 2022 Browse Articles

This Week In Chemistry Mars Past Oxygen Atmosphere And Hydrogen Fuel From Desalination Chemistry Chemical Structure Oxygen

Chemical Bonding Molecular Shapes And Vsepr Theory Britannica

Magnesium Description Properties Compounds Britannica



Comments
Post a Comment